How to Build a Secure Roof Design Construction for Houses | Roy Home Design
Before we build a roof, we should first get to know the structures and parts of the roof. The upper part of the house is called the roof. Its location far above often makes us less familiar with it.
Whereas, if viewed from the home function as a protector for occupants from the weather, then the presence of the roof was certainly can’t be ignored. In the tropics, we recommend the roof has a slope above 30° so that the rainwater can flow quickly. Want to know the roof even further? First, we have to know what components compose it.
The three constituent components of the roof are:
- Roof structure (roof truss and roof truss support);
- Roof cover (roof tile, polycarbonate);
- Roof complement (horizontal gutters/vertical gutters and molding, fascia board)
-
ROOF STRUCTURE
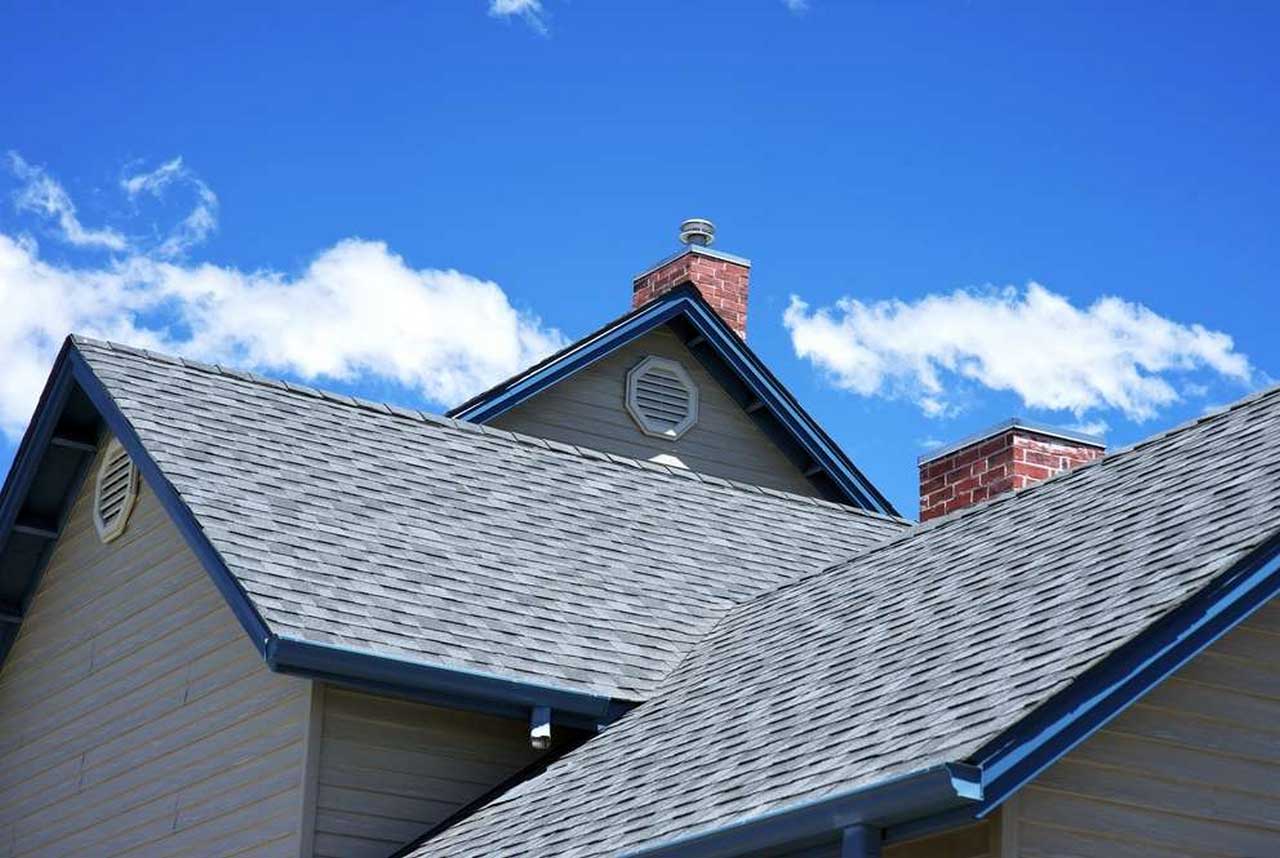
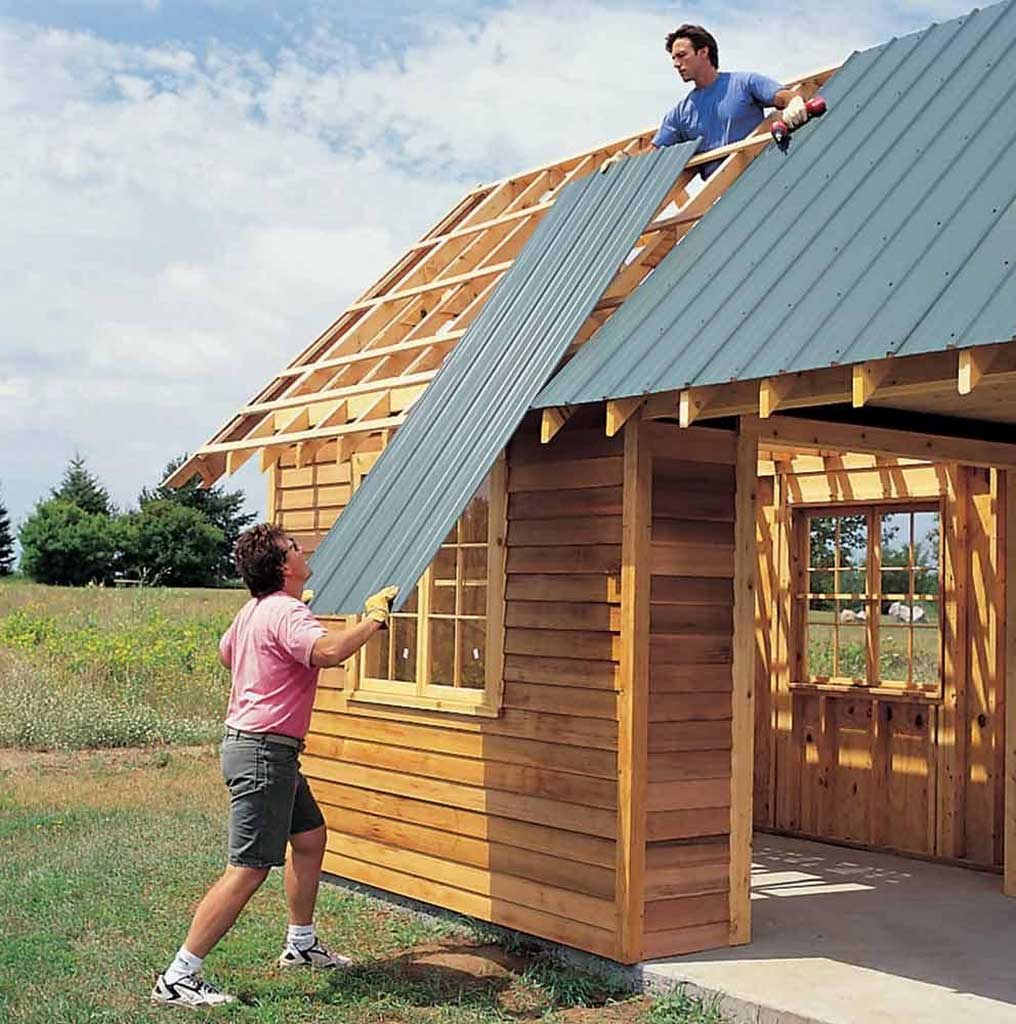
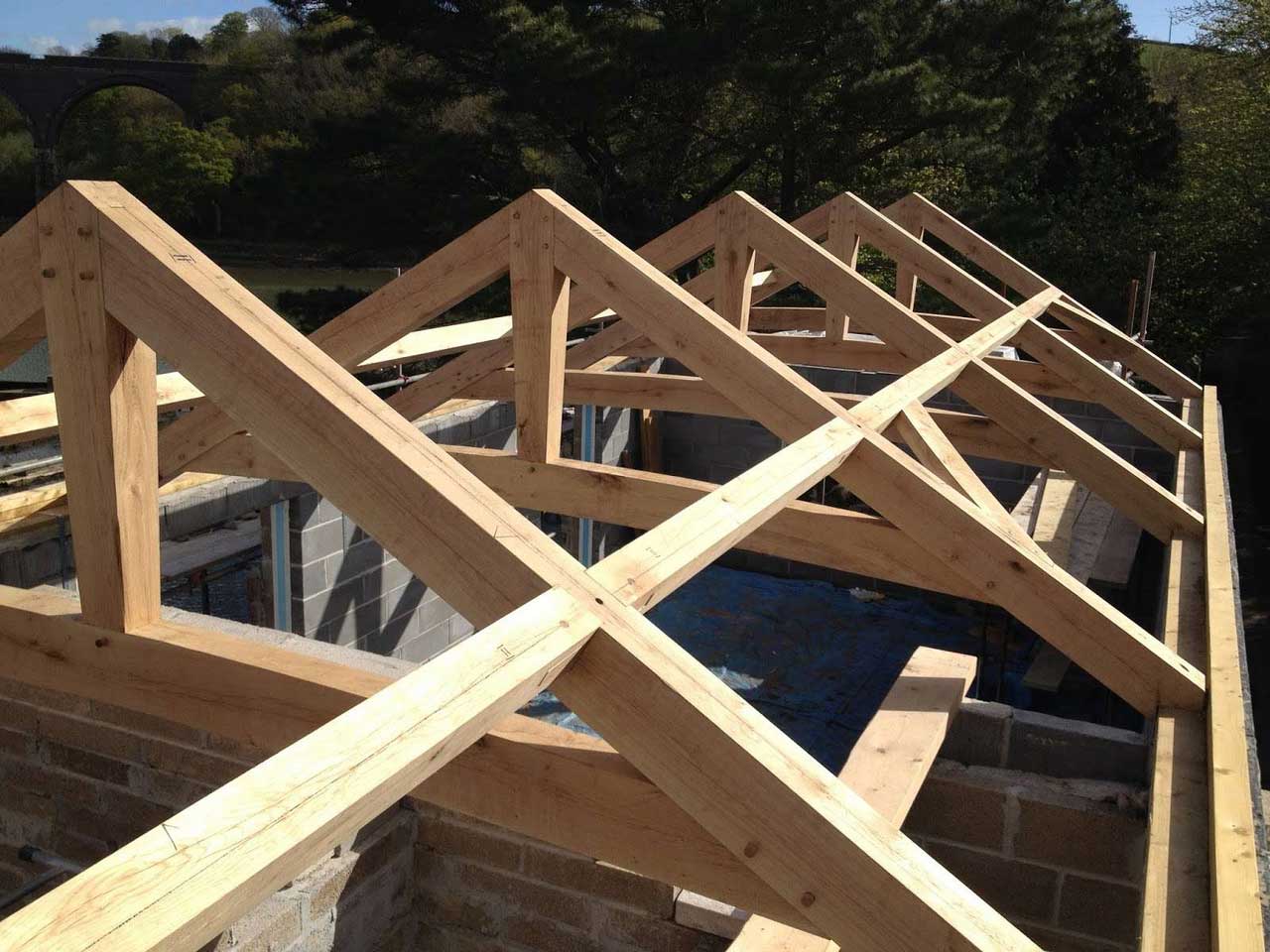
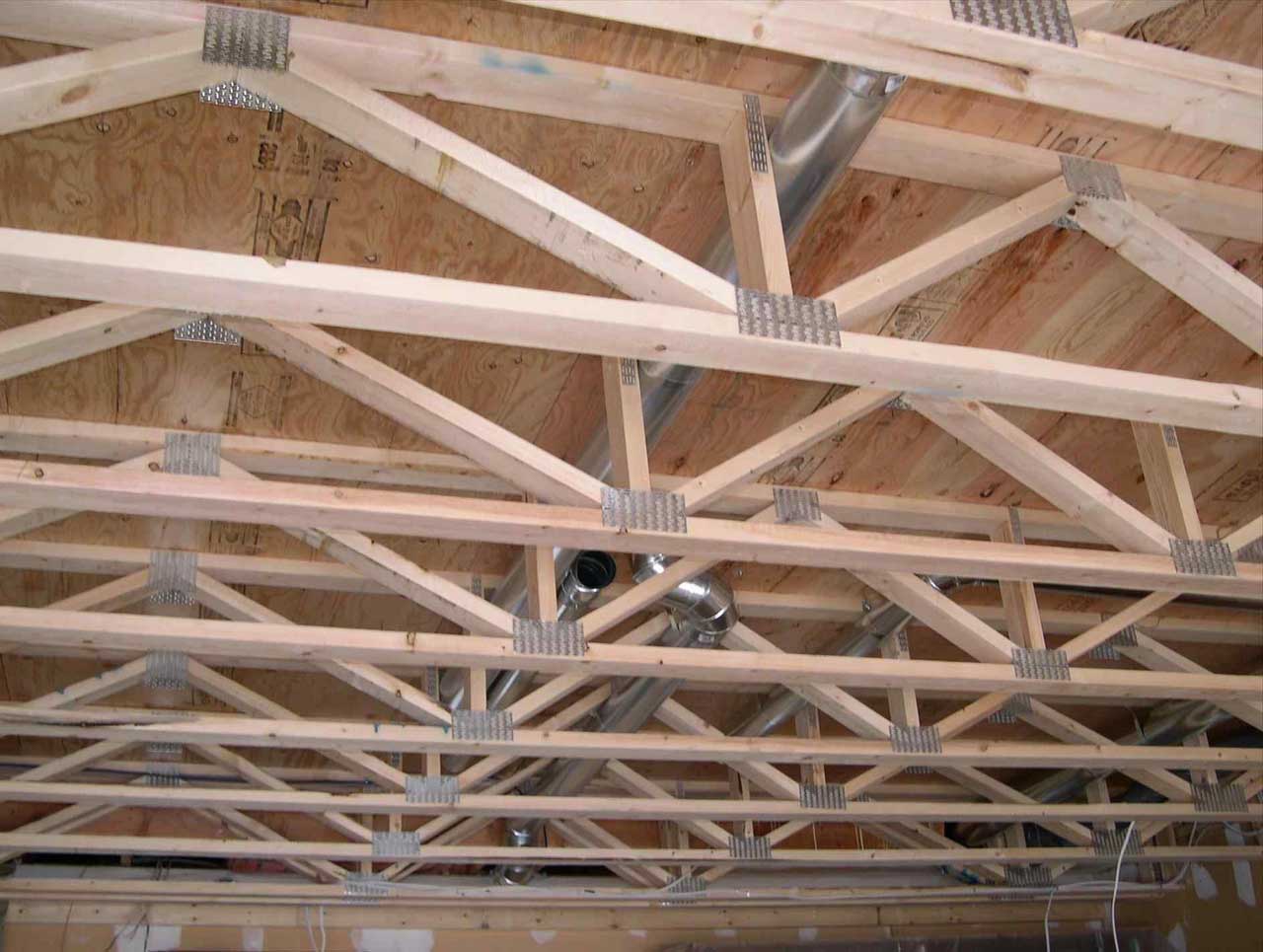
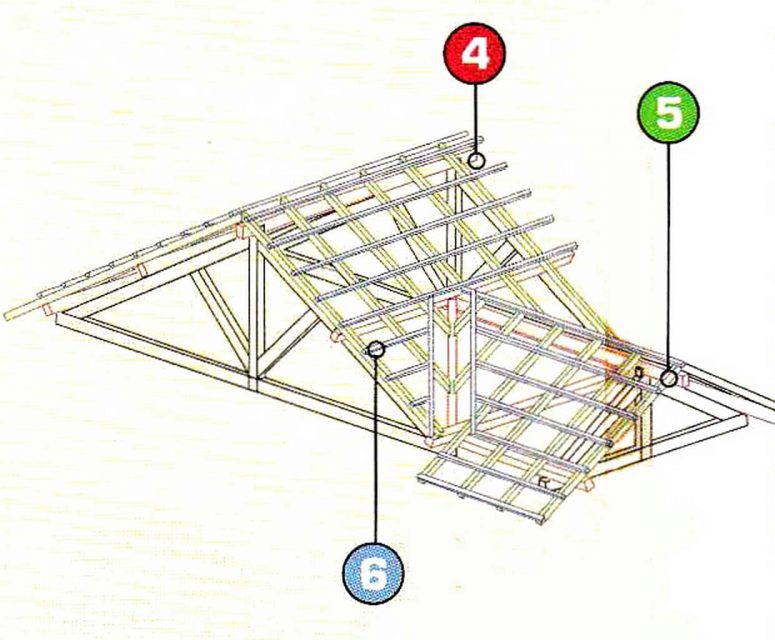
The definition of the roof structure is part of the building that became the foundation to hold the entire roof load. The roof structure is divided into a roof frame and roof frame support. The roof frame functions to hold the load from the roof covering material so that it is generally in the form of blocks (from wood/bamboo/steel) vertically and horizontally-except for the concrete flat roof structure. Based on this position, the terms purlin, rafter, and batten emerged. The roof frame arrangement can produce a groove on the roof (hip rafter/valley rafter) and create a certain roof shape.
Roof frame support is a wooden block arranged to form a triangle, called the roof truss. A roof truss is under the roof frame, its function is to support the roof frame. As a stiffener, the top of the roof truss is hooked on the ridge beam, while the two legs are connected to a column structure to deliver loads to the ground.
In general, there are 4 types of roof structures, namely: wall structure (flush gable roof) wood frame, truss and wooden frame, conventional steel structure, light steel structure. Beyond that, there is also a concrete roof structure commonly used for flat roofs.
Flush Gable Roof Structures
The presence of a roof truss can be replaced with a flush gable roof, which is an elevated house wall until reach the rooftop. The job of “the tall walls ” is the same as the roof truss, which supports the roof frame. Generally, flush gable roof is applied on the roof with gable model.
The Roof Parts
-
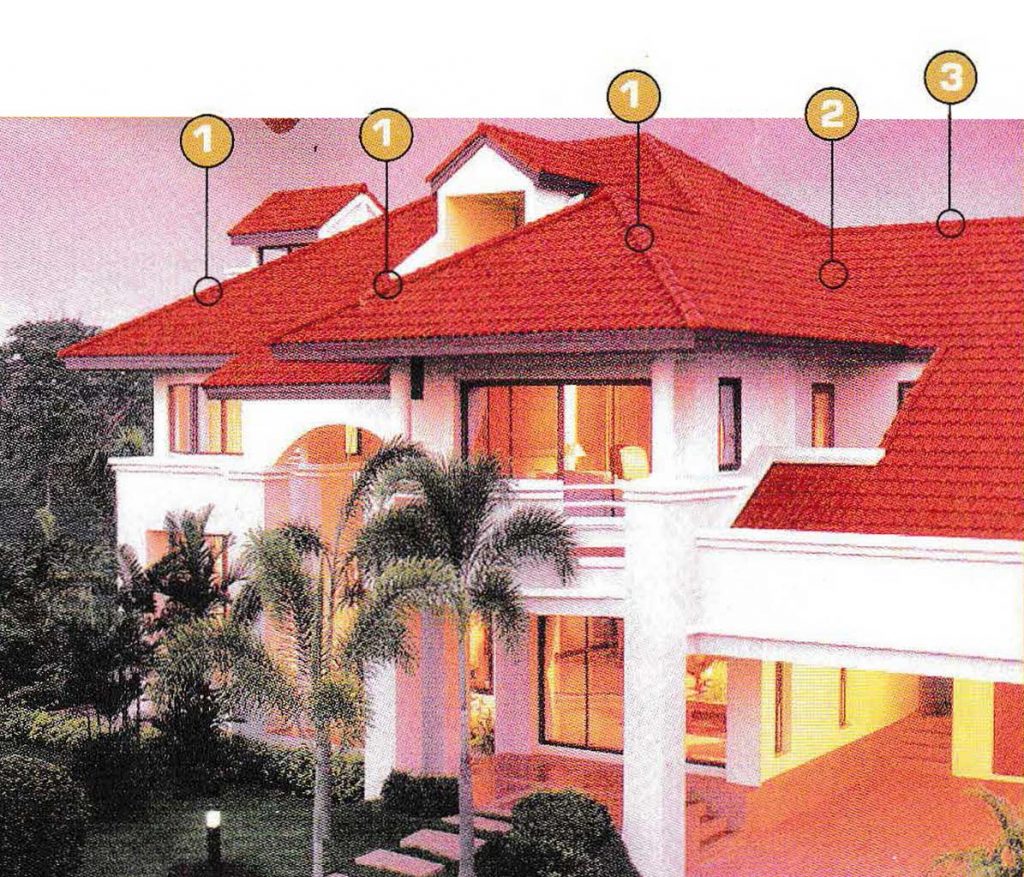
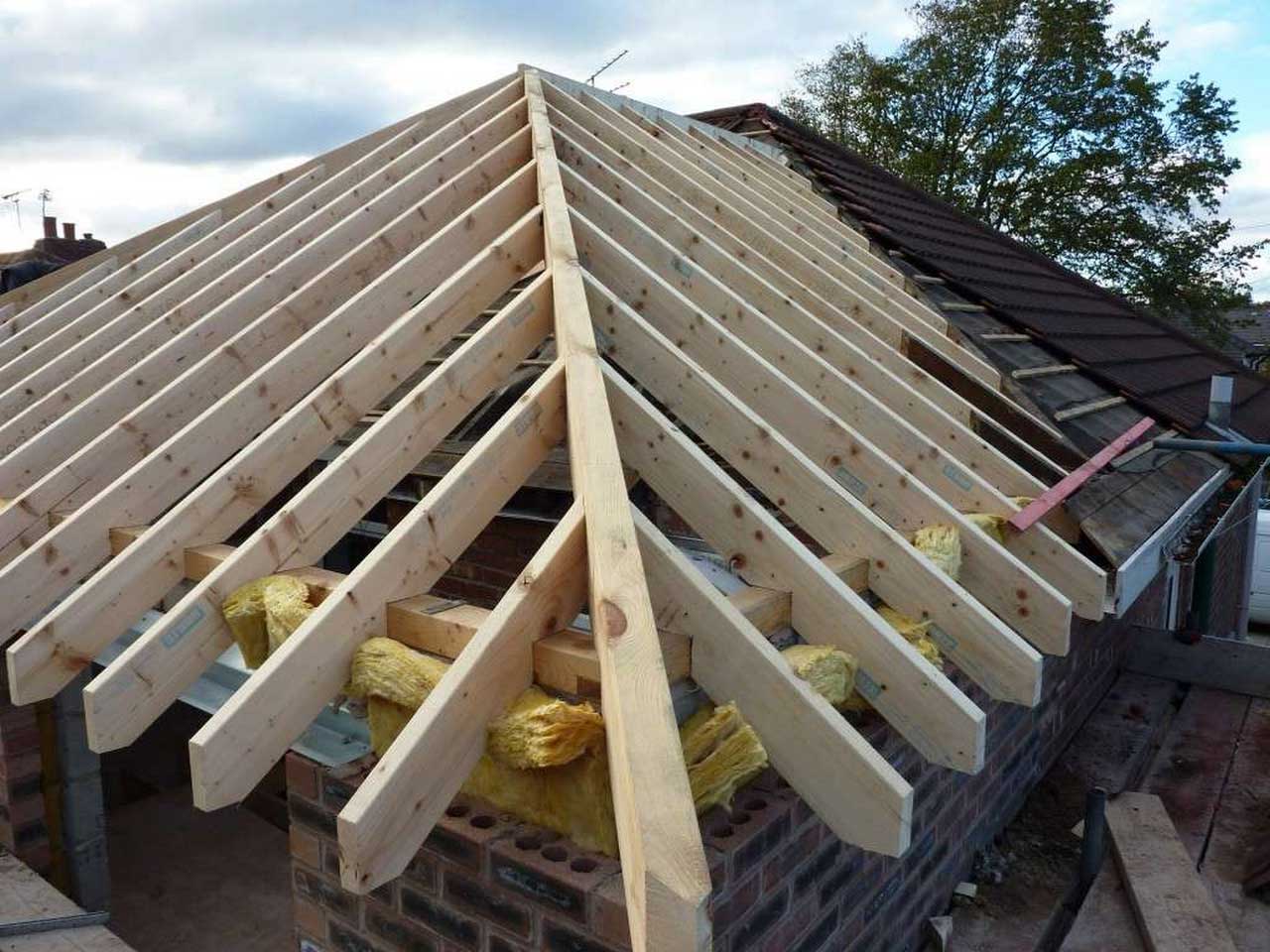
Valley Rafter
Valley rafter, is a sharp part of the roof, running from the edge of the roof up to the ridge, and is located at the confluence of two roof areas in the corner of the building inward.
-
Hip Rafter
The hip rafter, is a sharp part of the roof, running from the edge of the roof up to the ridge, found at the confluence of two roof areas at the corner of the building to the outside.
-
Ridge (Nok)
It is at the top of the roof, always flat and generally determines the direction of the building.
-
Purlin
Roof beam as a binder that connects between roof truss. Purlin is also a base for valley rafter and beam rafter.
-
The Rafters
Roofing components located on top of the rafters and be a stand for battens.
-
Roof Battens
Roof components that have the smallest profile in shape and size. Its position crosses (horizontal) over the rafter. Battens function as a cantilever to the roof cover (roof tiles and others). Another function is to channel the distance of each roof tile to be neat and more “bound”. The distance between battens depends on the size of the roof tile to be used. The bigger the dimensions of the roof tile, the less lath so the cost is more efficient.
-
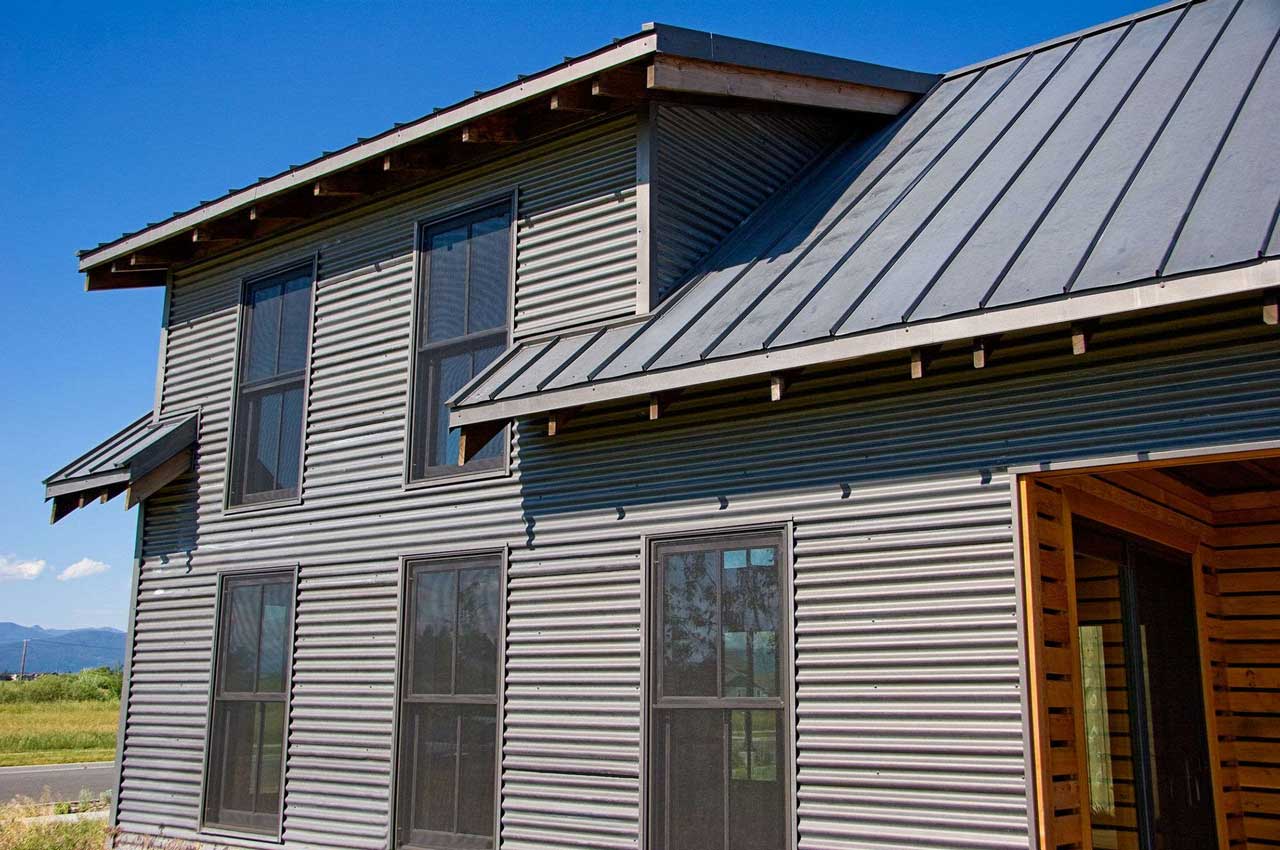
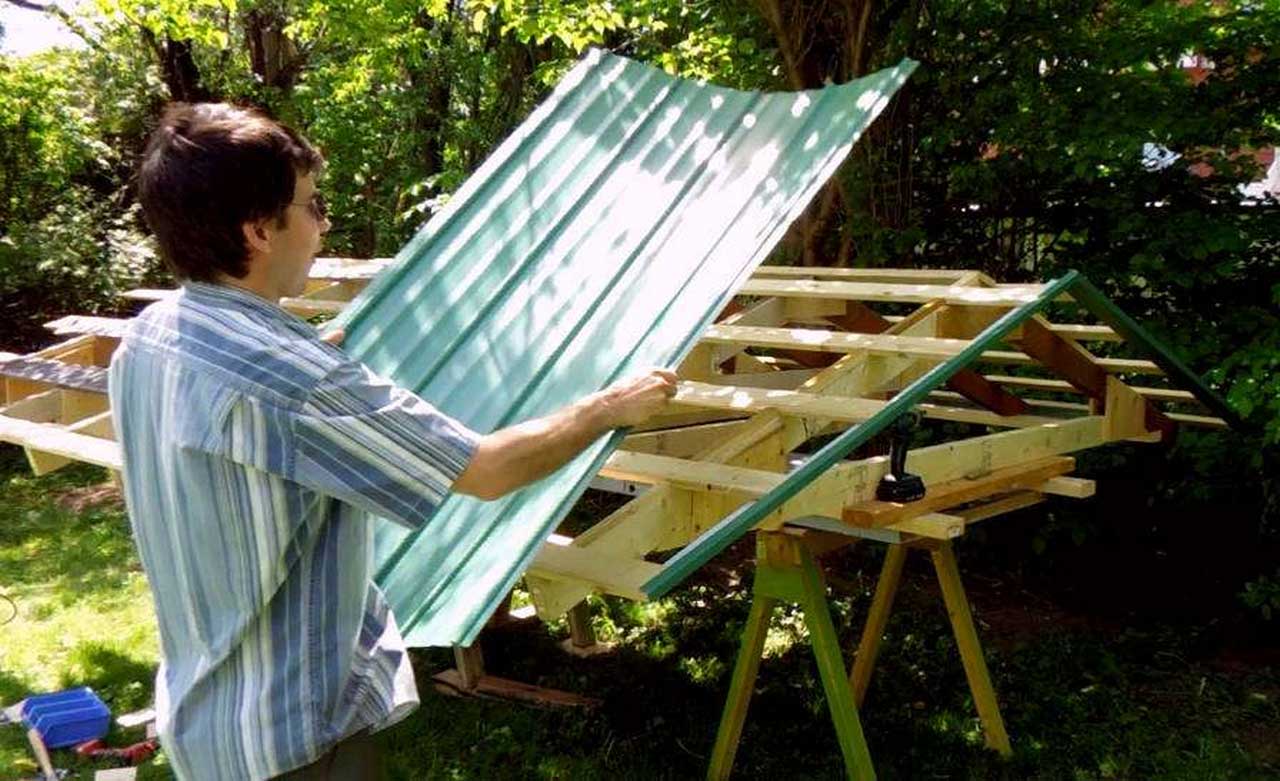
ROOF COVERINGS
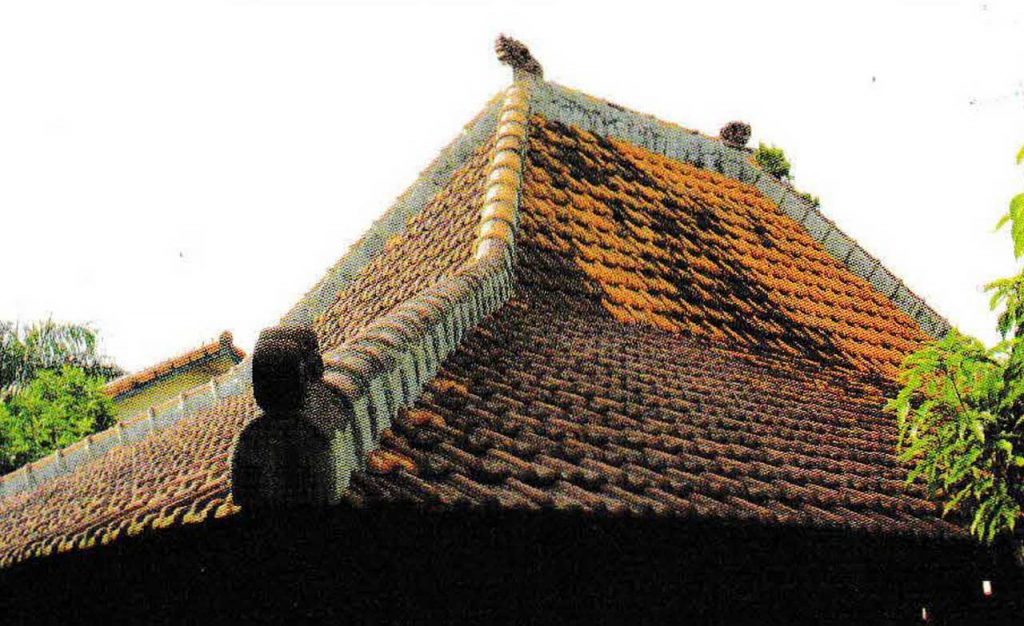

Roof tile: a group of small and solid elements that need a hanging batten. Polycarbonate roof: a large and translucent element (although somewhat reduced), this material only requires a ridge as a hanger. Shield roof type, the space below is cooler because there are cavities in it.
The roof cover is the part that covers the entire roof so that the upper threshold that limits us from the outside is created. There is a wide selection of roof coverings with a different variety of shapes and characters. The two main factors that must be considered to choose it are the material lightening factors so as not to overload the building structure and durability factors against the weather (wind, heat, rain). Another factor is compatibility/beauty with current home design. The size and design of the roof cover also give effect to the structure, for example, the construction of truss, lath size, and slope angle.
-
COMPLEMENT COMPONENT
The complementary elements of the roof beside functioning as a structural as well as aesthetics.
-
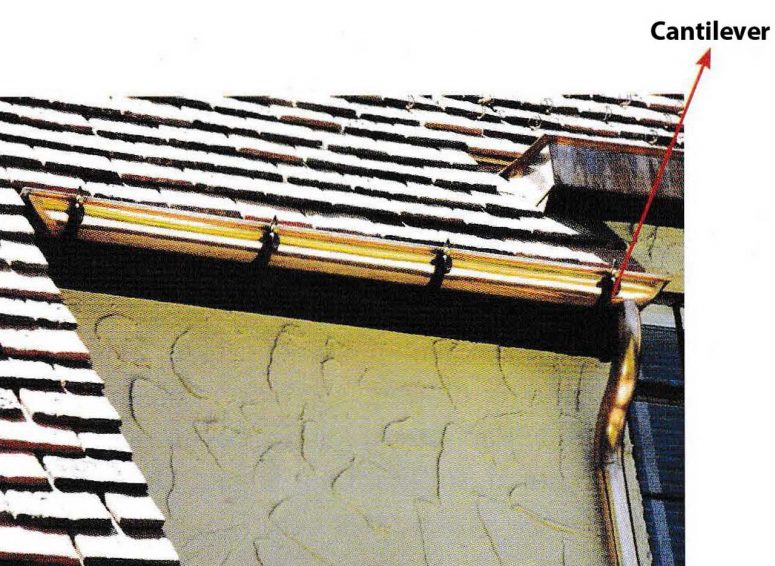
Gutters
Waterways on the roof that serves to direct water to fall to the ground are called gutters. Gutters mounted horizontally following the edge of the roof then flowed down through a vertical pipe. Gutters are given cantilever so that the position is solid.
-
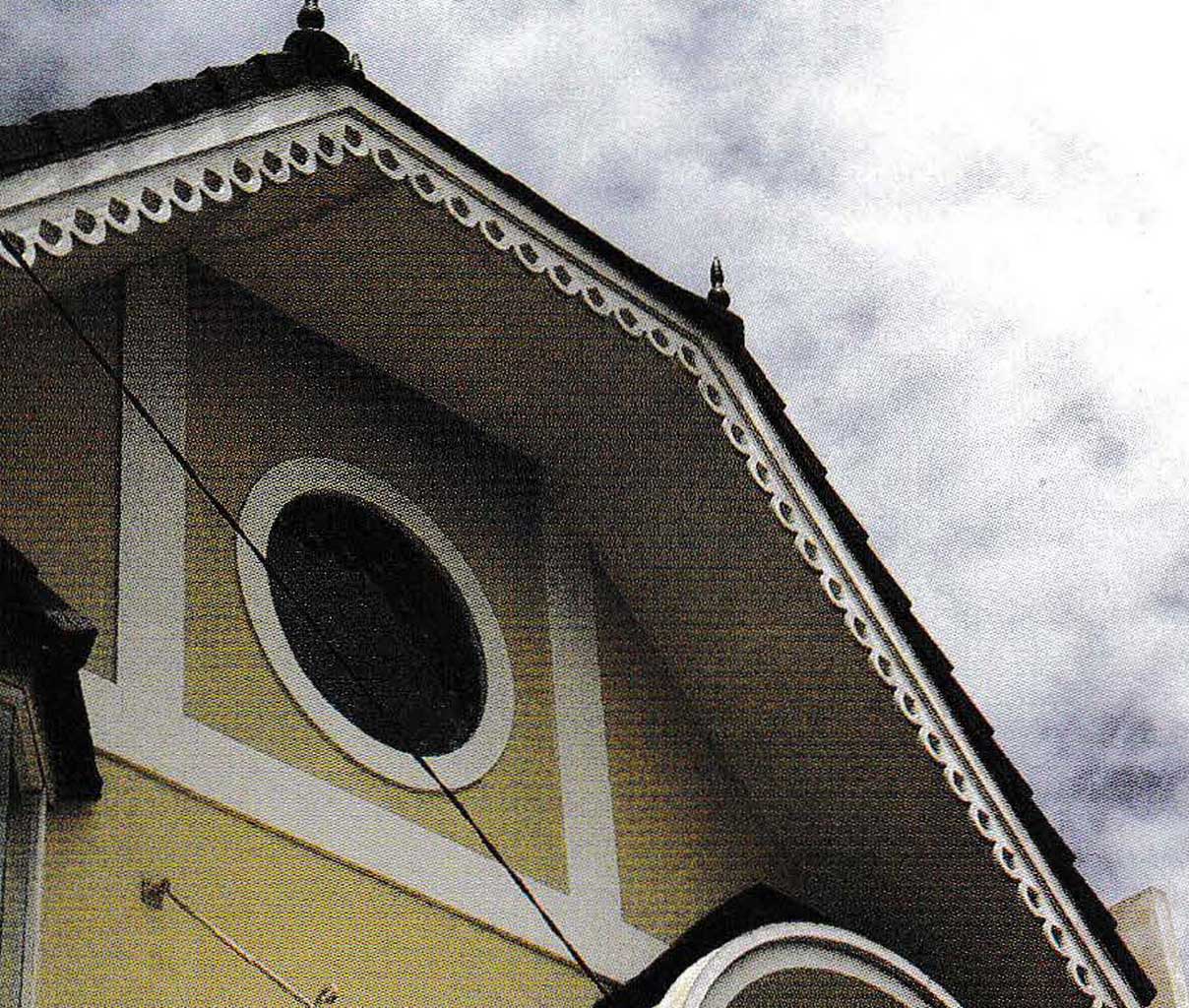
Fascia Board/Molding
In terms of construction, the fascia board creates a rigid formation (sturdy, unchanged) from the rafters arrangement. In the installation of the roof frame, the rafters are only held by nails and there is a possibility that the position will shift. This is where the fascia board functions to lock the arrangement of the rafter to stay in place. In terms of aesthetics, the fascia board/molding serves to cover the rafters which are lined up under the arrangement of roof tiles/other roof cover material. So, the appearance of the roof on the edge will look neatly by the presence of the fascia board/molding. Fascia boards that have a motive can add to the beauty of the roof.
DESIGNING A SECURE ROOF
Build a roof with secure construction has to be done carefully. The selection of materials and engineering installation of roof is a requirement to produce a secure roof. Small mistakes can cause big problems such as leaky roofs, extreme heat, and wood rotted.
The roof can be said to be of good quality if the structure is strong/sturdy and durable. Climate factors into consideration are important in designing the shape and construction of a roof/building.
The existence of a roof for a house is very important considering its function like an umbrella that protects the whole house building from weather disturbances (heat, rain, and wind). Therefore, a roof must be sturdy/strong and its strength depends on the supporting structure of the roof. Referring to climatic conditions, a secure roof design determined by 3 factors, namely the type of material, the shape and size of roof, and the workmanship technique.
Also read: Prevent a Leaky Roof from Water Damage
-
TYPE OF MATERIAL STRUCTURE AND ROOF COVERING
Determining material depends on the tastes of the occupants, but must still pay attention to the basic principles of a structure, which must be strong, precise, quite light, and not over design. A strong roof must be able to withstand the weight of all roof structure elements.
There are 3 types of weight coming from the roof, namely:
- The weight of the roof itself (frame material, frame support, and roof cover),
- Weight on pressure winds and suction winds, and
- Other moving weights (weight of human during installation and maintenance).
The choice of certain materials must be followed by complete knowledge of the characteristics in each material.
-
ROOF SHAPES & SIZES
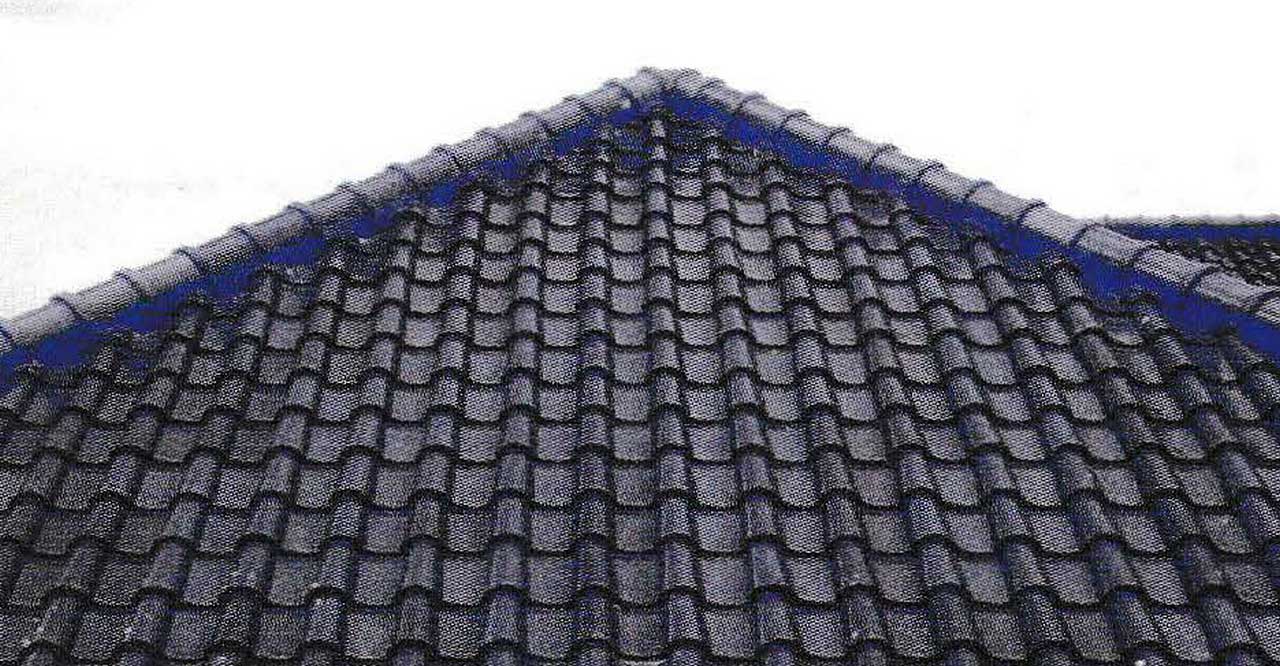 Compared to rain and heat, the wind was a factor that most anticipated to ensure a strong roof. Some problems due to strong winds include roof cover that flies, purlin detached, roof truss lifted, and wood columns shift or lift.
Compared to rain and heat, the wind was a factor that most anticipated to ensure a strong roof. Some problems due to strong winds include roof cover that flies, purlin detached, roof truss lifted, and wood columns shift or lift.
A good roof is that can receive the same wind loads from any directions (ideally a round shape roof). The shape of the roof is very influential on the magnitude of wind pressure that hit the building. The higher the building, the greater the wind pressure. Wind pressure works lighter when the height of the building is smaller than half the width of the building. The slope of the roof which provides a low wind load is between 10° – 30°. For angles greater than 30°, better strength and appropriate roof cover are needed.
Tips
Zinc roof cover and corrugated asbestos must be tied to purlin with nails of at least 6 nails per 1m². Roof tile cover must be fastened with wire every 5 lines of roof tile, while for roof tile there are holes that can be nailed to battens.
-
WORKING TECHNIQUES
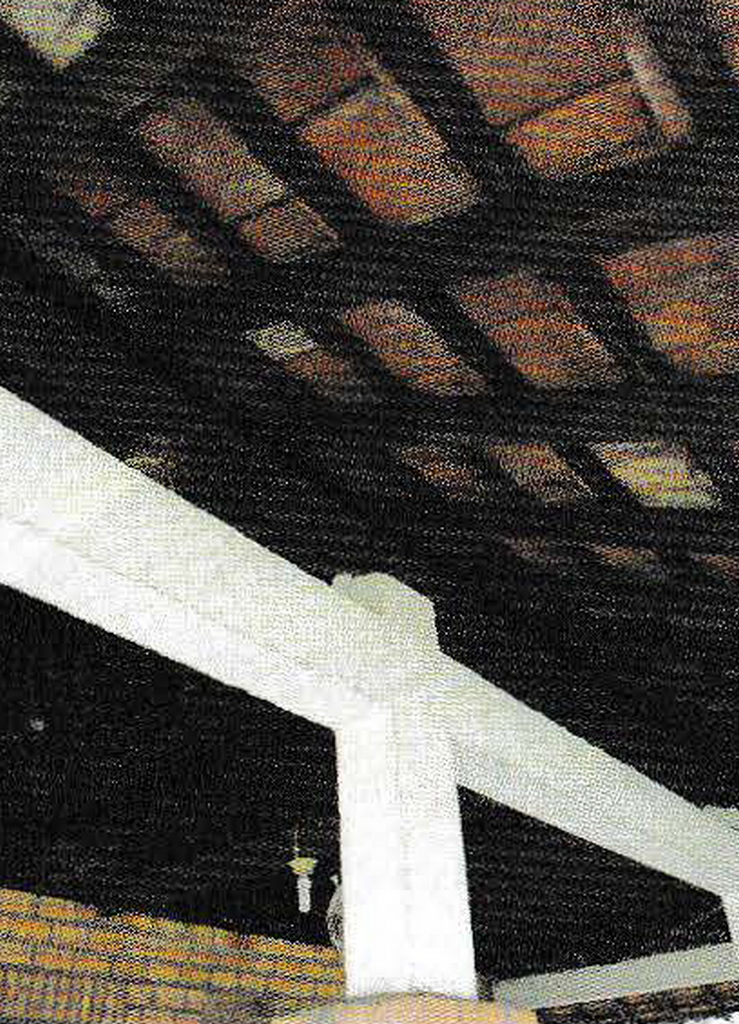 Roof installation must be made as carefully as possible in accordance with the rules and characteristics that follow each type of material. Some examples of the following requirements must be followed.
Roof installation must be made as carefully as possible in accordance with the rules and characteristics that follow each type of material. Some examples of the following requirements must be followed.
MAXIMUM SPAN
Each type of material has its own characteristics. Steel roof frame has a longer span ability than wood material. Steel or wood can be connected with a special connection by taking into account the dimensions/size of the beam and the forced behavior of the beam to be connected.
CONNECTION TECHNIQUES
The strength of the connection between the elements used for the frame must also be considered. For example, wood that has limited size, then a good and right connection is the key strength of the roof.
There are 2 kinds of methods to connect a wood, namely:
- Bolt. Bolts (without plates/with T plates/with L plates) choose the right diameter so that the wood does not break when bolted. The number of bolts is adjusted to the strength of the structure that will overload the connection and the wood dimension,
- Nail. The dimensions of nails are adjusted to the dimensions of wood, i.e. 2x the thickness of wood that is attached.
INSTALLATION
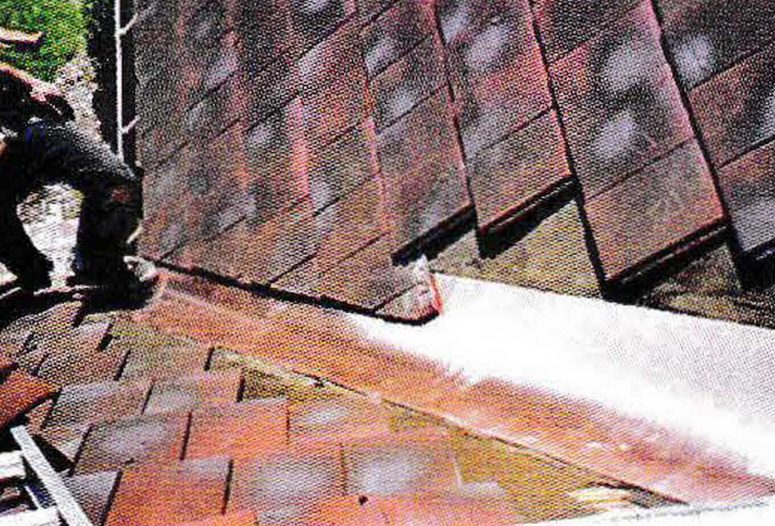 Tidy installation of the roof cover (precision), if using a roof tile, then the setting of the batten distance must comply with the specifications and recommendations of the manufacturer.
Tidy installation of the roof cover (precision), if using a roof tile, then the setting of the batten distance must comply with the specifications and recommendations of the manufacturer.
Some examples of inaccurate roof installation often occur in the valley rafter, namely the presence of buckling connections to the inside; roof structure that is not precise; or the corrugated area of the roof due to the installation of a not neat batten. All of this results in disturbances to the roof and affects the strength of the roof.
THE MATERIAL DURABILITY
 Whether the roof is durable or not is associated with environmental factors including weather and destructive organisms that can cause a decrease in structural capabilities. For example, termite attacks on wood. The wood that has been attacked will look intact even though the inside of the wood is porous.
Whether the roof is durable or not is associated with environmental factors including weather and destructive organisms that can cause a decrease in structural capabilities. For example, termite attacks on wood. The wood that has been attacked will look intact even though the inside of the wood is porous.
So, to create a strong roof, protection techniques for building materials are needed. For example, before using wood, treatment must be given that can increase the durability of wood. A metal material is usually given a special coating or coating that protects the material from corrosion or rust.
The tree that shaded roof is one way the inclusion of termites.
Also read: Prevent Termites Best Way How to get Rid of Termites
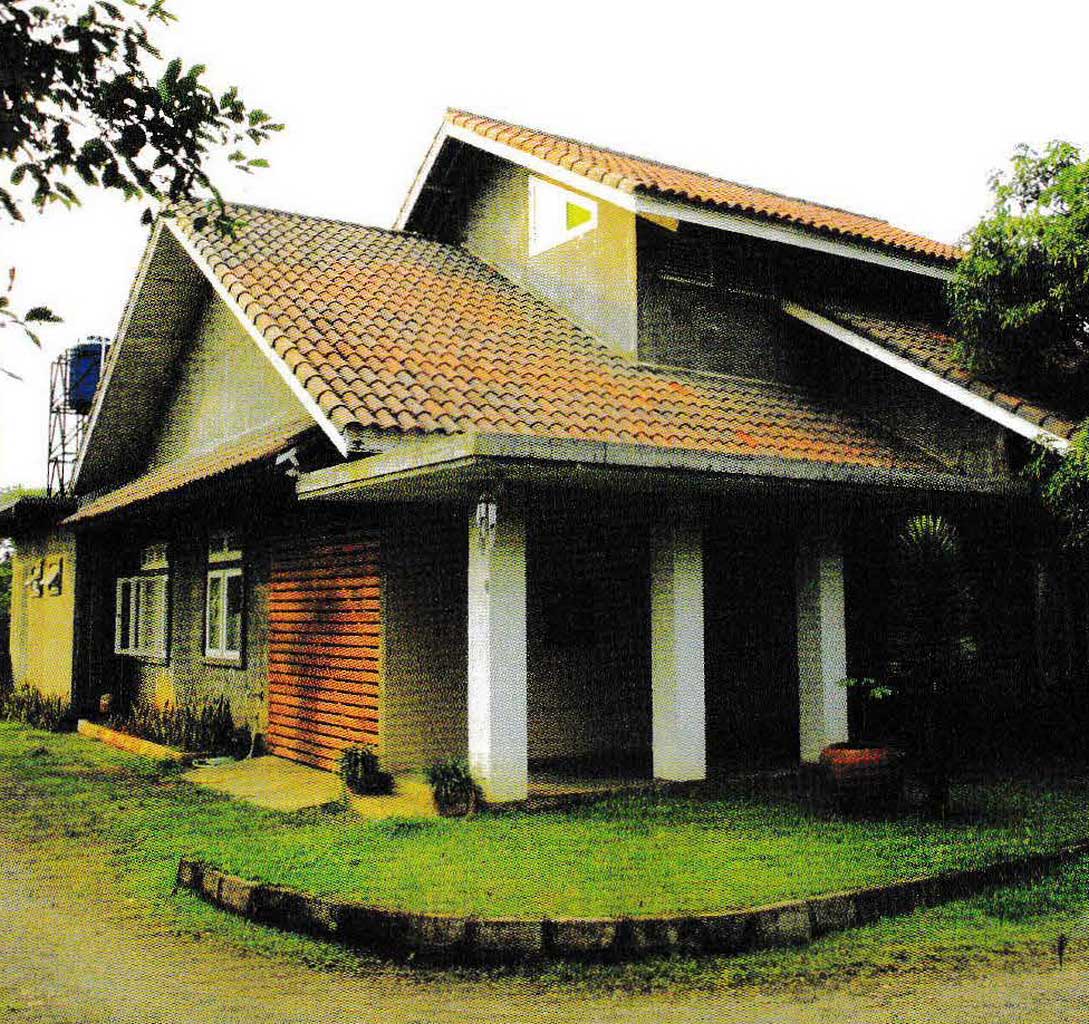
The Shape of Roof Based on Slope
- Flat roof (slope of 0° – 4°)
Character:
- simple in terms of manufacture and the appearance;
- cost per m² is cheaper (more efficient material usage);
- the room tends to be hot because generally, the flat roof uses metal material (has a low heat distribution so that the sun’s heat directly flows into the room);
- There are 2 types of cover, namely concrete roof and metal roof. The concrete roof is more expensive but the heat distribution is higher.
- The sloping roof, (the height of the roof is equal to/more than half the width of the building)
Character:
- roof construction is more complicated;
- requires a greater amount of material;
- the room below is cooler due to cavities in it;
- there are 2 choices of materials, namely clay (roof tile) and substitute materials such as concrete, bitumen, hardwood (shingle), and thin steel sheets formed like roof tiles;
- roof model options: gable, shield, cone, combinations of several types.
What about photograph previously mentioned? Is actually that awesome??? If you think thus, I’l d show you a few graphic yet again below:
So, if you’d like to obtain the outstanding photos about How to Build a Secure Roof Design Construction for Houses, click save link to download the shots for your personal computer. They’re prepared for transfer, if you’d rather and wish to obtain it, simply click save symbol on the article, and it will be directly saved to your notebook computer.
Here you are at our website, article above How to Build a Secure Roof Design Construction for Houses published. Lots of people attempting to find details about Build a Secure Roof Design and definitely one of these is you, is not it?